




ULTRASONICS
The branch of Physics which deals with study of ultrasonic waves is called Ultrasonic.
Ultrasound is acoustic (sound) energy in the form of waves having a frequency above the human hearing range. The highest frequency that the human ear can detect is approximately 20 thousand cycles per second (20,000 Hz). Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz.
Properties of Ultrasonic waves :
· The ultrasonic waves are high frequency sound waves.
· They are having smaller wavelength.
· They produce heating effect when passes through the medium.
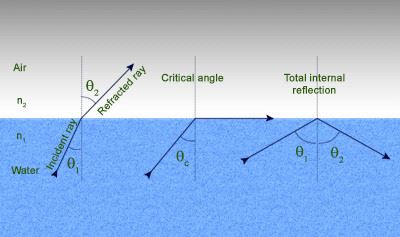
· They get reflected, refracted and absorbed by the medium similar to the ordinary sound waves.
· They act as catalytic agents to accelerate chemical reactions.
· They produce stationary wave pattern in the liquid while passing through it.
APPLICATIONS OF ULTRASONIC WAVES:
· Ultrasound can be used in sonar systems to determine the depth of the water in a location, to find schools of fish, to locate submarines, and to detect the presence of SCUBA divers.
· Echo Sounding :High powered ultrasonic pulses are emitted and received back after reflection from the obstacle. Depth of Sea is calculated by this method. Moreover, detrection of sunk ships and submarines is also done.
· Diagnostic use: – Such waves are used to detect tumourous, soft tissue structures, lesions, and abnormal growth in the body.
· Sterilisation purposes: – Ultrasonic waves destroy living organism like bacteria or even small insects.
· Drilling Holes: – Ultrasonic drills are used for machining (making holes/attening shapes etc) aluminium, titanium, tungsten, molybdnem, mica, granite etc.
· Ultrasonic cleaning : – Components to be cleaned are immersed in a washing solution of trichloroethylene and ultrasonic oscillations are excited in it. Boiler scums are removed. Walls of petroleum wells are de-paraffined. Remotest pores are cleaned.
· Coagulation : – Fine particles of dust, smoke, ash, fog etc collide against each other and bind formines bigger particles when subjected to Ultrasonic waves. This method is employed by industries to remove smoke from industrial stack, acid fumes etc.



Comments are closed.