1st Law of Thermodynamics
The branch of Science(physics) which deals with the transformation of heat energy into other forms of energy and vice-versa is called thermodynamics.
OR
The study of heat and its transformation to mechanical energy is called thermodynamics.
OR
Thermodynamics is the study of interactions between heat and other forms of energy.
Thermodynamics is derived from Greek words thermos which means ‘heat’ and dynamics which means ‘power’.
Thermodynamic System:-

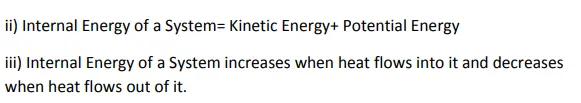

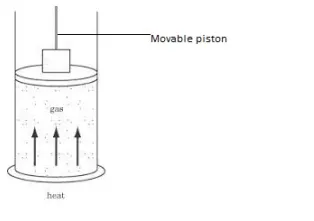
Internal energy of an ideal gas (molecules with no or negligible intermolecular force) depends only on temperature.
Internal energy=Kinetic energy +potential energy
As it is an ideal gas, there is no intermolecular force between the molecules, so the potential energy is zero.
Hence,
Internal energy=Kinetic energy
In practice or reality no gas is ideal. There is always some deviation from ideal behaviour.
Mechanical Equivalent Of Heat
Introduction:-
i) Whenever Mechanical work is done on a system, Heat is produced.
ii) Work and Heat are interconvertible i.e Heat can be expressed in terms of Work and Work can also be expressed in terms of Heat.
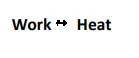
JOULE’S LAW
Statement :- Whenever Work is converted into Heat or Heat is converted into Work, the quantity of Heat disappearing in one form is equivalent to the quantity of energy appearing in the other form.
Thus work and heat are directly proportional to each other.




Comments are closed.