Dimension & Dimensional Formula Of Physical Quantities
Dimensions:
Dimensions of a physical quantity are, the powers to which the fundamental units are raised to get one unit of the physical quantity.
The fundamental quantities are expressed with following symbols while writing dimensional formulas of derived physical quantities.
· Mass →[M]
· Length→[L]
· Time→[T]
· Electric current →[I]
· Thermodynamic temperature →[K]
· Intensity of light →[cd]
· Quantity of matter →[mol]
Dimensional Formula :
Dimensional formula of a derived physical quantity is the “expression showing powers to which different fundamental units are raised”
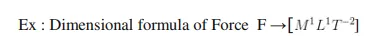
Dimensional equation:
When the dimensional formula of a physical quantity is expressed in the form of an equation by writing the physical quantity on the left hand side and the dimensional formula on the right hand side, then the resultant equation is called Dimensional equation.
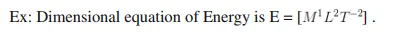
Derivation of Dimensional formula of a physical quantity:-
The dimensional formula of any physical quantity can be derived in two ways.
i) Using the formula of the physical quantity :
Ex: let us derive dimensional formula of Force .

ii) Using the units of the derived physical quantity.
Ex: let us derive the dimensional formula of momentum.

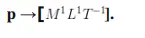
Quantities having no units, cannot possess dimensions:
The following physical quantities neither possess units nor dimensions.
Trigonometric ratios, logarithmic functions, exponential functions, coefficient of friction, strain, poison’s ratio, specific gravity, refractive index, Relative permittivity, Relative permeability.
Quantities having units, but no dimensions :
The following physical quantities possess units but they do not possess any dimensions.
Plane angle, angular displacement, solid angle.
Quantities having both units & dimensions :
The following quantities are examples of such quantities.
Area, Volume, Density, Speed, Velocity, Acceleration, Force, Energy etc.
Physical Constants :
These are two types
i) Dimension less constants (value of these constants will be same in all systems of units):
Numbers, pi, exponential functions are dimension less constants.
ii) Dimensional constants (value of these constants will be different in different systems of units):
Universal gravitational constant (G),plank’s constant (h), Boltzmann’s constant (k), Universal gas constant (R), Permittivity of free space( ) , Permeability of free space ( ),Velocity of light (c).



Comments are closed.