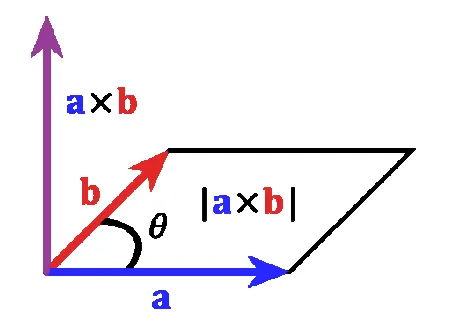
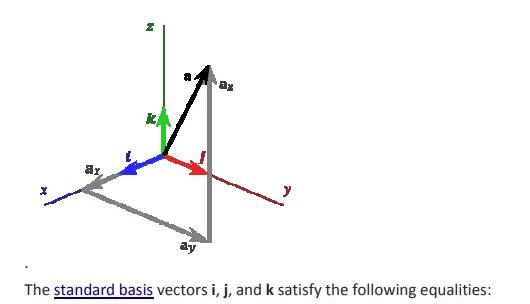
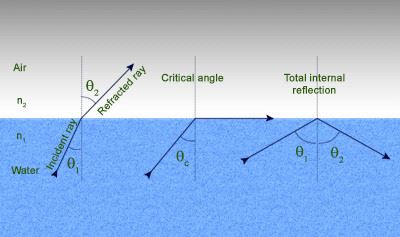
The cross product of two vectors a and b is defined only in three-dimensional space and is denoted by a × b.
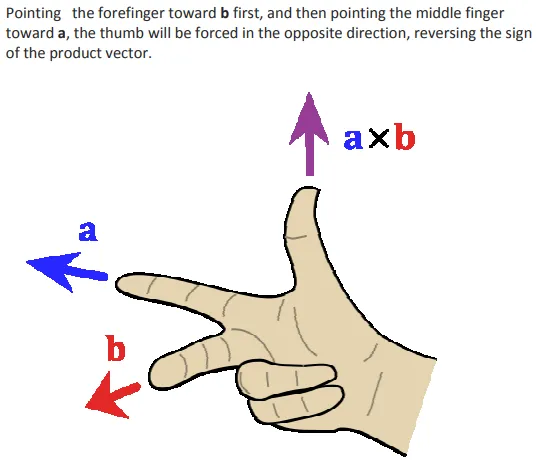
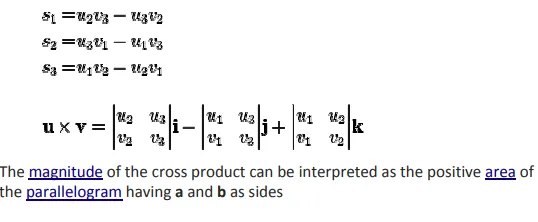
The cross product a × b is defined as a vector c that is perpendicular to both a and b, with a direction given by the right-hand rule and a magnitude equal to the area of the parallelogram that the vectors span.